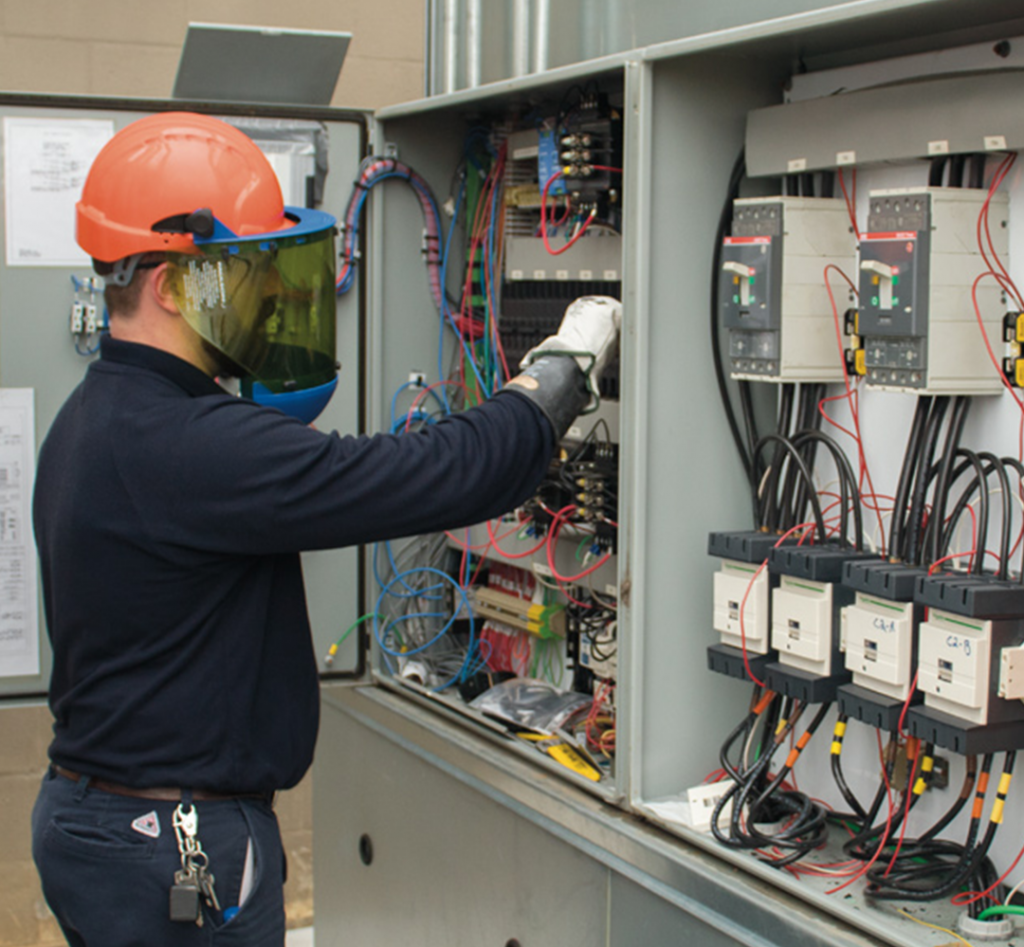

Electrical Maintenance
Why it’s important to address Electrical maintenance?
- Cost Savings
- Reduce Damages and Human Loss
- Insurance companies could deny claims for negligence
- Increase Efficiency
- Lower maintenance costs
- Monitoring the aging of the equipment
- Support Regulatory Compliance
Preventive Maintenance
Often called “calendar-based maintenance”. Repairs or maintenance actions are taken on machinery on a scheduled basis, regardless of actual condition of equipment.
Benefits:
- 50% of electrical failures can be prevented with regular maintenance and inspection
- Increased equipment life
- Reduced equipment failure
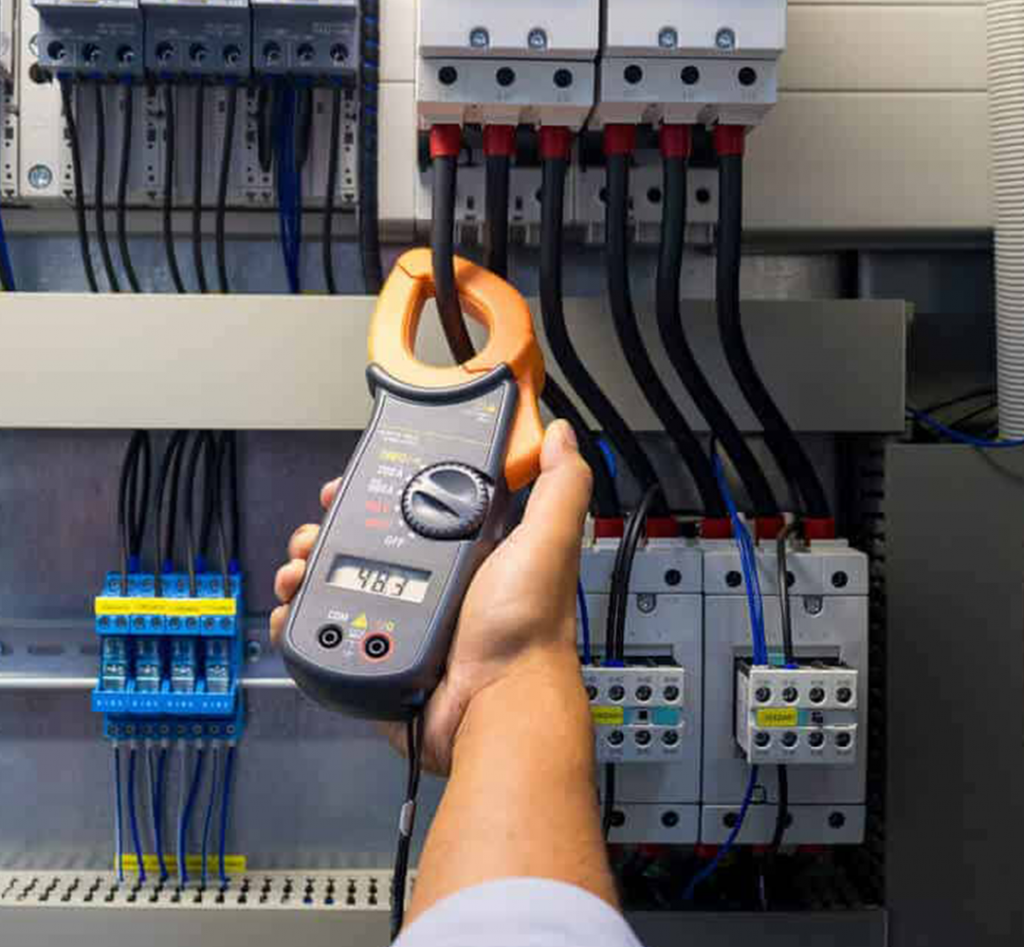


Reactive Maintenance
Often called “run to failure” No repair or maintenance actions are taken on machinery until the designed life span is reached or other variables cause the machinery to fail.
Benefits:
- Unexpected costs, sometimes catastrophic, downtime and overtime hours
- Secondary damage caused by failure
- Risk of higher capital costs
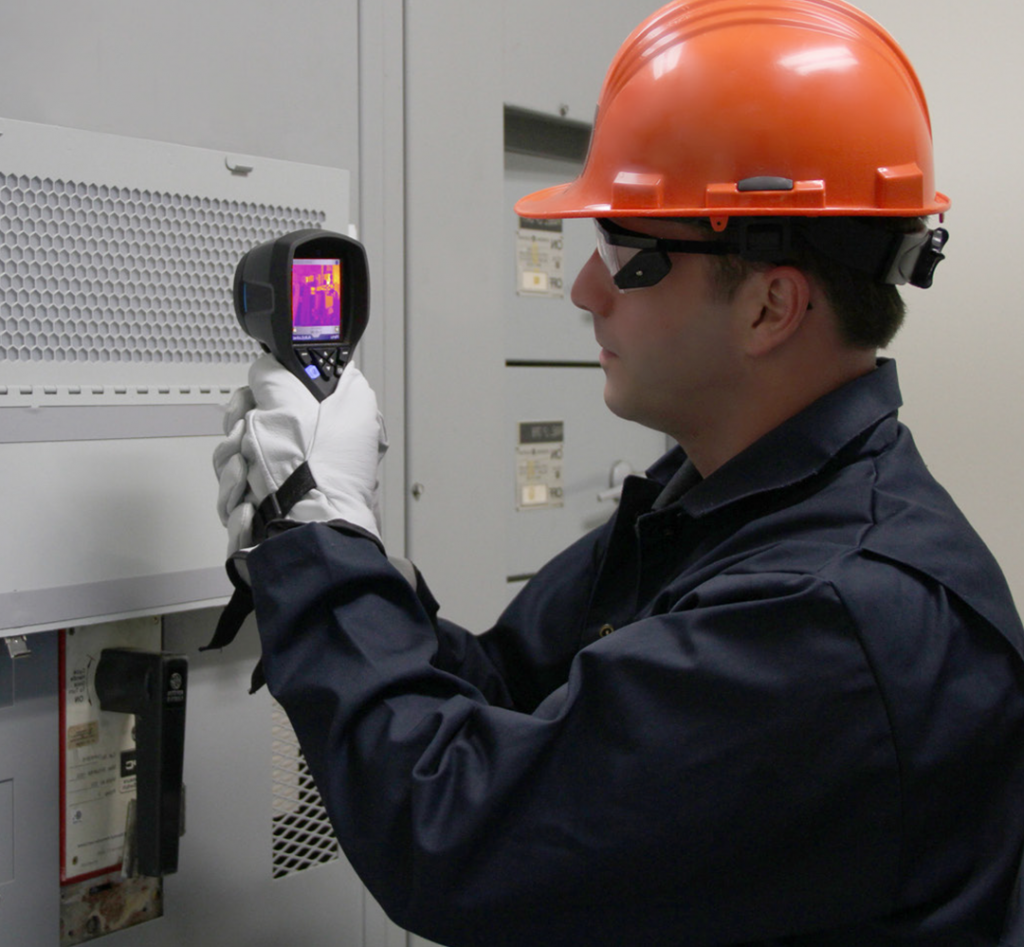
Predictive Maintenance
Often called “condition-based maintenance”. Repairs or maintenance actions are taken based on changes in machine performance, monitored over time with various test equipment.
Benefits:
- Equipment is serviced when needed
- Lowest repair part and expedite Costs
- Increased equipment life
- Reduced equipment failure

Safety
Failure of electrical and mechanical components could be catastrophic, injuring or even killing employees, maintenance personnel or the public.

Greater asset reliability
Realized by locating the problems prior to failure which greatly reduces unscheduled outages, associated equipment damage and down time.

Increased revenue
With more uptime, revenue is maximized. With less maintenance on good components and faster repairs of faulty components, maintenance costs are reduced leading to a better bottom line.
